Assalamualaikum Warahmatullahi Wabarakatuh
Aligned with one of the IP’s commitments to be part of the global community, all college students can join our classes through the Virtual Student Exchange Program. In this program, you will meet notable lecturers who have exceptional expertise in the Industrial Engineering field. These classes will become a valuable way to catch the recent knowledge, insights, and experiences to enrich your understanding and perspective.
Several courses are offered to International Students around the globe.
As you register, you will enroll in the NON-DEGREE program for 1 semester and be eligible for a temporary Student ID. A Certificate of Completion will be issued following the end of the course with min 80% class attendance and earn min of B grade. Table 1 depicts the class timeline.
Tabel 1. Timeline
Term |
1st Session Meetings |
Mid Term Exam(UTS) |
2nd Session Meetings |
Final Exam(UAS) |
| Odd Term 2021/2022 | Sept 27 – Oct 28, 2022 | Nov 2-11, 2021 | Nov 15 – Dec 24, 2021 | Dec 28, 2021 – Jan 10, 2022 |
| Even Term 2021/2022 | March 7 – April 22, 2022 | May 12 – 27, 2022 | June 30 – July 15, 2022 | July 19 – 29, 2022 |
The following are the list of offered courses for the odd term 2021/2022
COURSE DESCRIPTION
BIG DATA ANALYTIC
Managing information flow for accurate and fast response decision making in the Artificial Intelligence era is very challenging today. New technologies, devices, and social applications are revolutionizing data management in many domains of activities in business, public administration, and scientific research. Types of data are getting complicated. Organizations must face a massive amount of data on a daily basis ranging from text, images, sound, video (multimedia) coming from many sources of online and offline transactions. We are in the Big Data world. Big Data is continuously changing the way organizations run their businesses.
Organizations need to improve their ability to understand and analyze big data to take full advantage of its power in making the right and timely decisions such as strategic decision making and identify new business opportunities. Also, a massive level of information raises the high demand for data scientists and business analysts to help organizations gathering and analyzing data insights.
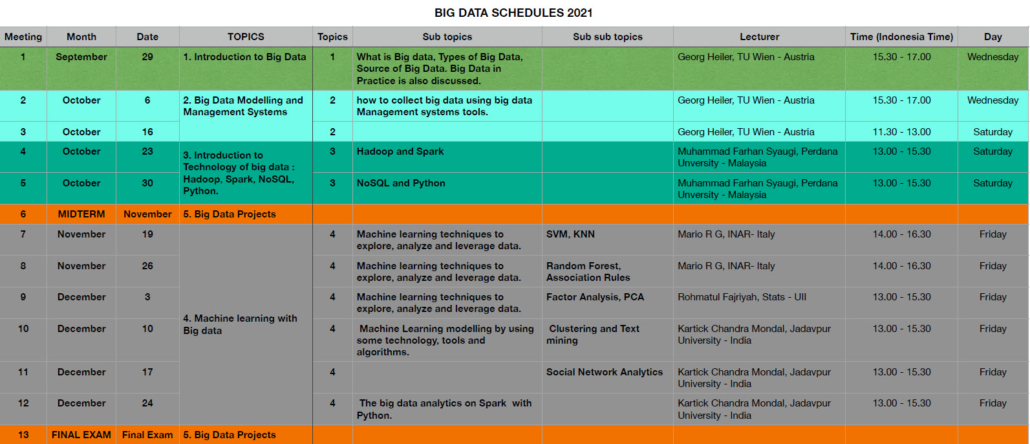
This course is designed to learn how big data is organized, analyzed, and interpreted for enhancing decision making. Some practical big data analytic will be discussed for understanding what insight big data. This course will explore big data in practice and the tools and technology employed to manage big data in an organization.
Course Outline:
- Introduction to Big Data. Topics such as What is Big Data, Types of Big Data, Source of Big Data, Big Data in Practice will be discussed.
- Introduction to Technology of big data: Hadoop, Spark, NoSQL, Python, R.
- Machine learning with Big dataThis topic will introduce machine learning techniques to explore, analyze, and leverage data. Some technology and tools and algorithms will be discussed to create machine learning models. The big data analytics will use algorithms that run on Spark with Python. This topic also discusses Predictive Analytics, Descriptive Analytics, and Social Network Analytics.
- Big Data Projects
Source :
- Baesens, Bart. Analytics in a Big Data World. The Essential Guide to Data Science and its Applications. John Wiley & Sons. 2014. Dasgupta, Nataraj. Practical Big Data Analytics. Packt Publishing. 2018.
- Dasgupta, Nataraj. Practical Big Data Analytics. Packt Publishing. 2018.
- Deitel, Paul J. Intro to Python for Computer Science and Data Science. Learning to Program with AI, Big Data, and Cloud. Pearson Education.2020.
- Marr, Bernard. Big Data in Practice. How 45 Successful Companies Used Big Data Analytics to Deliver Extraordinary Results. John Wiley & Sons.2016.
INDUSTRIAL INTERNET OF THINGS (IIoT)
(FREE ENROLLMENT CLOSED)
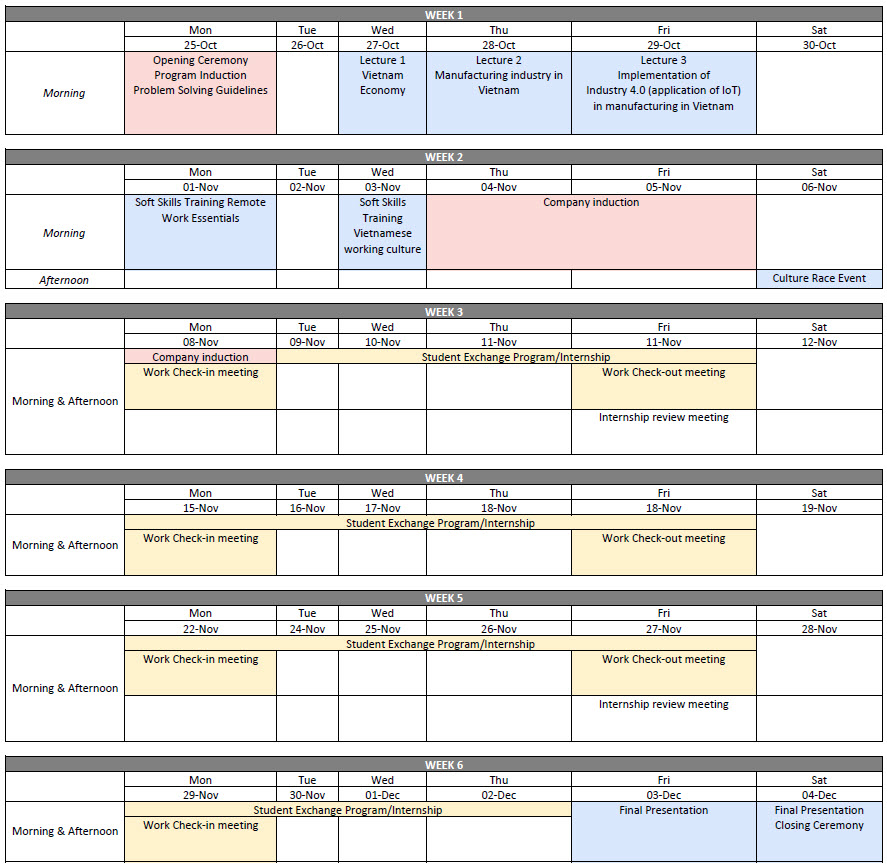
This course is intended to study the implementation of IoT in the Industry. Students will work on an IoT-based project or any projects from companies in Vietnam. The students will be exposed to an international working environment in which they are going to work on a project collaborating with students from other countries such as Japan, and Australia and training new skills. Programming Logic and Statistic is a prerequisite.
This course is almost similar to the internship program. The difference is that each student doesn’t have to submit an official internship report to the department. The grade will be based on the performance of your work to complete the project. Hence, students must be committed to perform well during the program.
The followings are the detailed course information :
- Program Description
- List of Companies
- Submit your CV to complete the program. It is recommended that you polish and update the CV as it will be sent to potential companies.
- Agenda/Schedule
The application will be forwarded to potential host companies.
Upon the receiving of a confirmation letter from the host companies, Students are notified through email.
It takes approximately 1-2 weeks to process and place the companies before starting the program.
An Internet connection and a laptop are required to conduct the Virtual Internship.
The orientation program will be started as the first program session supervised by a Program Coordinator to best introduce the company.
Each student will be assigned a Program Coordinator who will accompany, support, and supervise from the beginning of application until the internship completion.
Working hours will be varied and range from 20 to 40 hours a week depending on assigned projects.
Outcome-based will be the performance measurement of this program. Some possibilities of commitment and workload can be discussed further with the host companies.
A certificate of completion will be released by the host companies.
INTELLIGENT SYSTEMS
In the intelligent System course, students will learn about artificial intelligence and its implementation. After learning this course, students will understand the definition of an intelligent system and its role in the industry. Students are also able to develop expert systems and implement artificial intelligence techniques to solve industrial cases.
Students will learn :
Meetings :
Meeting 1 : Introduction to the intelligent system and its application in industry 4.0
Meeting 2 : Knowledge extraction and introduction to Expert System: rule-based system
Meeting 3 : Application of rule-based Expert System using Python programming language
Meeting 4 : Frame-based Expert System
Meeting 5 : Application of Frame-based Expert System
Meeting 6 : Introduction to Fuzzy Logic and Fuzzy Expert System
Meeting 7 : Application of Mamdani-style Fuzzy Inference System
Meeting 8 : MID EXAM
Meeting 9 : Sugeno-style Fuzzy Inference System and its application
Meeting 10 : Artificial Neural Network: Perceptron and its application
Meeting 11 : Multilayer Neural Network
Meeting 12 : Application of Artificial Neural Network using Python programming language
Meeting 13 : Genetic Algorithms – Part 1
Meeting 14 : Genetic Algorithms – Part 2
Meeting 15 : Application of Genetic Algorithms using Python programming language
Meeting 16 : FINAL EXAM
SYSTEM MODELLING
This course provides an understanding of modeling system concepts for the students and guides them to be able to turn the real system into a mathematic model by giving prior comprehension on the concept of system and model. Therefore, the learning system is firstly more emphasized with lecture method and group assignment for three to four students. The topics in the first part of the course include the definition and kinds of systems, definition, and characteristics of models, kinds of models (deterministic and stochastic), the stages of model development, mathematic modeling, parameter estimation, and model verification and validation. In the second part of the course, the students will need to conduct a practice on modeling a real system through a major project for 3 to 4 persons.
The objectives of this course are :
- Understand the fundamental of System Modeling
- Evaluate the most proper model to solve previously formulated problems.
- Develop simple Mathematical Models for system optimization by formulating existing system problems.
- Develop discrete and deterministic mathematical models for system optimization.
By learning this course, students will :
- understand modeling concepts, system modeling, discrete and continuous system modeling, Deterministic & stochastic system modeling, and mathematical modeling.
- be able to explain system thinking concept, simulation modeling, generative system thinking modeling approach, knowledge engineering system modeling, conceptual model design, and behavior analysis modeling and the model decision making.
To achieve the objectives, meetings will discuss :
- System Thinking
- System Concepts
- Problem Formulation
- Problem Formulation Tools: Rich Picture Diagram
- System Modeling
- System Modeling Tools: Causal Loop Diagram
- MID EXAM
- Discrete deterministic modelling
- Heuristic modeling
- Model Analysis and Validation
- Complex Theory
- Complex System: Discrete Event Simulation
- Complex System: Agent-Based Modeling
- Complex System: System Dynamics
- FINAL EXAM
PROGRAMMING LOGICS
As the fourth industrial revolution looms, intelligent devices such as robotics and computers with intelligent computations received major attention from industry and academicians. Computer programming and logics skill become the main competence for industrial engineers. This course provides basic logics knowledge to trigger the logic of students in constructing algorithms. A software to prove the logic will also be utilized. The python programming language will be intensively practiced expressing the logic of solving real problems. Therefore, students will be able to evaluate their logic on the spot and acquire python skills as a prerequisite of more advanced courses such as Machine Learning, Intelligent Systems, Big Data analytic, and Data Science as required industry 4.0 skills. In the end, students will have a big project to develop an application and promote their application to encourage users to use the application.
PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL I
Manufacturing planning and control (MPC) covers strategic and tactic activities in a manufacturing system. At the strategic level, MPC starts from demand management until ordering techniques determination. It would be continued by tactic level which is controlling activities on the production shop floor to ensure that the plan could be executed well. This subject focuses on techniques at a strategic level that are demand management and forecasting, aggregate planning, product mix, and master production schedule, material requirements planning, and inventory control for independent and dependent demand. This subject is the predecessor subject for Production Planning and Control – 2, which focuses on tactic-level activities in MPC.
Meetings :
Meeting 1 : Introduction to manufacturing planning and control.
Meeting 2 : Demand management and forecasting.
Meeting 3 : Forecasting (continued) and validation
Meeting 4 : Aggregate planning.
Meeting 5 : Aggregate planning (continued).
Meeting 6 : Product mix and master production schedule.
Meeting 7 : Rough cut capacity planning
Meeting 8 : MID EXAM
Meeting 9 : Material requirements planning.
Meeting 10 : Capacity requirements planning.
Meeting 11 : Inventory for dependent demand.
Meeting 12 : Inventory for dependent demand (continued)
Meeting 13 : Inventory for independent demand.
Meeting 14 : Inventory for independent demand (continued)
Meeting 15 : Application of planning activities in a manufacturing system.
Meeting 16 : FINAL EXAM
PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL 2
Production planning must be followed by controlling activity to ensure planned and allocated resources could be managed more effectively and efficiently. This subject covers machine scheduling in flowshop and jobshop environment as successor activities after Material Requirements Planning, Assembly Line Balancing, Purchasing, and several production engineering techniques such as Theory Of Constraints (TOC) as system ongoing improvement paradigm, Just In Time philosophy (JIT), Cellular Manufacturing System and Flexible Manufacturing System. An engineering data analysis based on Industry 4.0 concept is also introduced to students as an idea trigger to support the undergraduate thesis.
Meetings :
Meeting 1 : Introduction to controlling activity in manufacturing planning and control.
Meeting 2 : Computer Aided Process Planning
Meeting 3 : Scheduling: single machine and flowshop scheduling
Meeting 4 : Scheduling: job scheduling (shifting bottleneck heuristic)
Meeting 5 : Assembly Line Balancing with 5 methods
Meeting 6 : Purchasing
Meeting 7 : Introduction to supply chain management
Meeting 8 : MID EXAM
Meeting 9 : Just In Time (JIT): concept and application
Meeting 10 : Lot-bucket MRP in JIT
Meeting 11 : Theory of Constraints: the diagrams
Meeting 12 : Theory of Constraints: Drum Buffer Rope
Meeting 13 : Cellular Manufacturing System: Group Technology
Meeting 14 : Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS): scheduling in FMS
Meeting 15 : Introduction to industry 4.0: engineering data analysis
Meeting 16 : FINAL EXAM
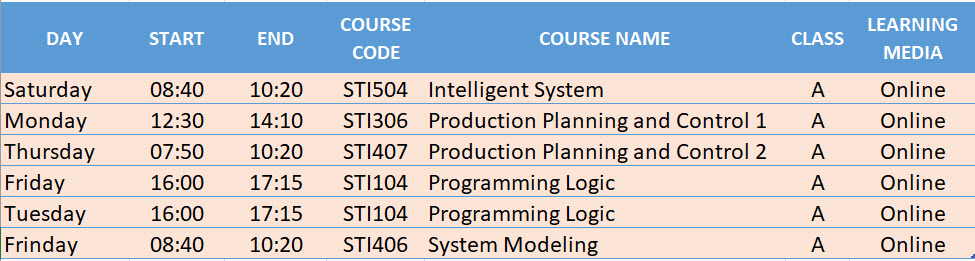
SCHEDULE